
#Lumen definition biology series#
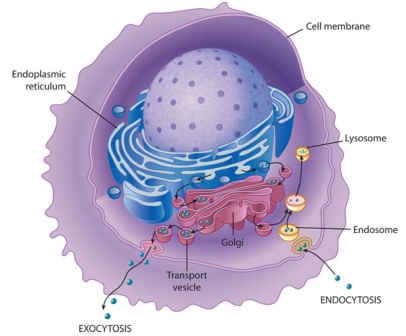
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) (Figure 1) is a series of interconnected membranous tubules that collectively modify proteins and synthesize lipids. A darkly staining area within the nucleus, called the nucleolus (plural = nucleoli), aggregates the ribosomal RNA with associated proteins to assemble the ribosomal subunits that are then transported through the nuclear pores into the cytoplasm. We already know that the nucleus directs the synthesis of ribosomes, but how does it do this? Some chromosomes have sections of DNA that encode ribosomal RNA. When the cell is in the growth and maintenance phases of its life cycle, the chromosomes resemble an unwound, jumbled bunch of threads, which is the chromatin. For example, in humans, the chromosome number is 46, whereas in fruit flies, the chromosome number is eight.Ĭhromosomes are only visible and distinguishable from one another when the cell is getting ready to divide.
Every species has a specific number of chromosomes in the nucleus of its body cells. In eukaryotes, chromosomes are linear structures. This combination of DNA and proteins is called chromatin. Chromosomes are structures within the nucleus that are made up of DNA, the hereditary material, and proteins. To understand chromatin, it is helpful to first consider chromosomes. The nuclear envelope is punctuated with pores that control the passage of ions, molecules, and RNA between the nucleoplasm and the cytoplasm. Both the inner and outer membranes of the nuclear envelope are phospholipid bilayers. The nuclear envelope is a double-membrane structure that constitutes the outermost portion of the nucleus (Figure 1). (credit: modification of work by NIGMS, NIH) Notice that the nuclear envelope consists of two phospholipid bilayers (membranes)-an outer membrane and an inner membrane-in contrast to the plasma membrane, which consists of only one phospholipid bilayer. The outermost boundary of the nucleus is the nuclear envelope. Let us look at it in more detail (Figure 1). The nucleus (plural = nuclei) houses the cell’s DNA in the form of chromatin and directs the synthesis of ribosomes and proteins. Typically, the nucleus is the most prominent organelle in a cell (Figure 1). numerous membrane-bound organelles-such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and othersīecause a eukaryotic cell’s nucleus is surrounded by a membrane, it is often said to have a “true nucleus.” The word “organelle” means “little organ,” and, as already mentioned, organelles have specialized cellular functions, just as the organs of your body have specialized functions.

Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: Our natural world originated the principle of form following function, especially in cell biology, and this will become clear as we explore eukaryotic cells. For example, a skyscraper should be built with several elevator banks a hospital should be built so that its emergency room is easily accessible. In architecture, this means that buildings should be constructed to support the activities that will be carried out inside them. Have you ever heard the phrase “form follows function?” It’s a philosophy practiced in many industries. What you’ll learn to do: Identify membrane-bound organelles found in eukaryotic cells


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
